What is a Balance Sheet?
Also known as your “Statement of Financial Position”, a Balance Sheet reports a company’s assets, liabilities and equity at a specific point in time. It is usually complemented with 2 other financial statements to evaluate a business. They are the “Income Statement” and “Statement of Cash Flows”.
These financial statements can easily be prepared by accounting service providers like us, to save companies resources, allowing them to focus on other key operations.
Purpose of a Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet provides various insights for business owners and investors alike. It can inform users of the financial health of a business, and an overview of what the company owns and owes.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/balancesheet.asp-V1-5c897eae46e0fb0001336607.jpg)
Essence of a Balance Sheet
A Balance Sheet is split into 2 sections, and as its name suggests, both sides should always be equal. It is to be compared with those of previous periods and benchmarked against other businesses in the same industry. The Balance Sheet also allows users to derive financial ratios to assess the company’s finances.
In this section of the article, we will be breaking down some of the elements of a Balance Sheet.
1. Assets
In this segment of the Balance Sheet, accounts are listed in ascending order, depending on its liquidity. This means that the assets that are easiest to be converted into cash will be listed first.
Assets will also be divided into current and non-current. Current assets can be converted into cash within a year or less, while non-current requires a longer time. This is a common order in which current assets are listed:
- Cash & cash equivalents – Can include treasury bills and short-term certificates of deposit.
- Marketable securities – Any equity and debt securities with maturities that tend to be less than one year.
- Accounts receivables – Money that you have yet to collect from customers, including an allowance for customers that may be unable to pay.
- Inventory – Goods available for sale.
- Prepaid expenses – Value that has already been paid for. Eg: Insurance, Rent, etc.
Common order for non-current assets:
- Long-term investments – Securities that cannot be converted to cash within a year.
- Fixed assets – Involves land, machinery, equipment, buildings, etc.
- Intangible assets – Involves non-physical assets such as intellectual property and goodwill.
2. Liabilities
Liabilities are the money that the business owes others. It can includes bills to suppliers, interest on bonds, wages and salary of employees, etc. The concept of current liabilities is similar to that of current assets.
Current liabilities are those that are due within one year and are listed in order of their due date. Common examples of current liabilities include:
- Accounts payable – Any amounts the company owes others.
- Utilities payable
- Rent
- Interest payable – Interest on loans, bonds, etc.
- Wages payable – Staff salaries
- Dividends payable – Accounted if your company pays dividends to stockholders.
- Other accrued expenses
On the other hand, non-current liabilities can include:
- Long-term debt – Involves interests and principal on bonds issued.
- Deferred tax liabilities – Taxes that have been accrued but will not be paid until the next year.
- Other long term obligations
3. Shareholder’s Equity
This refers to the net worth of the company. It involves money that a business owner or its shareholders invested into the business. Some common elements of shareholder’s equity include:
- Retained earnings – Net earnings after a company reinvests in the business or pays off debt.
- Common stock – A security that represents ownership in a corporation.
- Preferred stock – Preferred stockholders have a higher claim to dividends or asset distribution compared to common stockholders.
Sample Balance Sheet
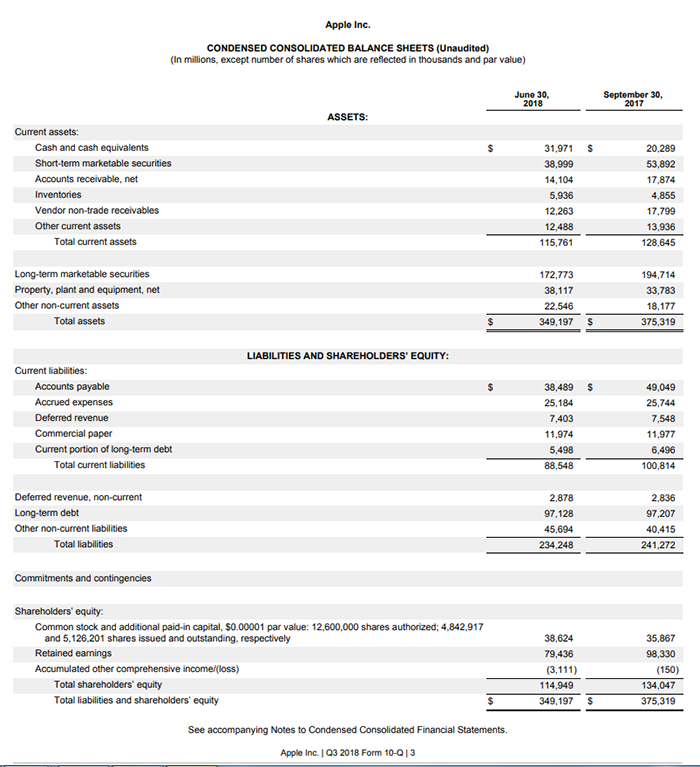
It takes some time to be able to differentiate the individual aspects listed under a Balance Sheet. Understanding what each line means for your business is the same. However, at Count On Me, we have Senior Accountants readily available to advice you on cost reduction and cash flow improvement at a glance! Feel free to reach out to us for a consultation and we will get back to you as soon as we can.
Alternatively, check out some of our other relevant articles here!


